Target Locked: The Rising Case for Defense in Private Markets - Part 3
The global security landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with supply chains being redrawn and national sovereignty concepts being redefined in real-time.
Defense investment is transitioning from an edge case to core investment consideration for many LPs.
This is the last part of a three-part blog series that delves into defense investing within the private markets context – if you missed them, Part 1 provided a market overview of the opportunity and Part 2 looked deeper into the evolution of ESG and infrastructure opportunities.
“The best time to plant a tree was 20 years ago. The second best time is now.”
Chinese Proverb
Executive Summary
- Defense investing is transitioning from taboo to strategic theme, requiring sophisticated manager selection and robust policy frameworks for success
- Exit strategies are evolving with strategic acquirers and public markets showing increased appetite for defense-focused businesses
- Emerging technologies including quantum computing, hypersonics, and biotechnology represent the next frontier of defense investment opportunities
- Success requires clear LP frameworks, appropriate manager selection, and sophisticated risk management capabilities that exceed ‘normal’ investing standards

The Future Landscape of Defense Investment
Traditional taboos surrounding defense investing are fading as LPrs recognise the sector’s role in supporting stability, resilience, and democratic values. LPs will increasingly be asked to justify their position on defense exposure and articulate the logic behind their allocation decisions – whether doing so or not!
The convergence of private market dynamism and strategic defense needs presents compelling opportunities for investors seeking to contribute to national security whilst pursuing significant returns. This alignment of financial and strategic objectives creates a powerful investment thesis.
Success in defense investing requires careful manager selection, robust policy frameworks, and sophisticated risk management capabilities. Investors who develop these competencies will be well-positioned to capture attractive opportunities whilst supporting broader security objectives.
Emerging Technology Frontiers
The next generation of defense technologies presents unprecedented investment opportunities across multiple cutting-edge domains. Quantum computing applications in cryptography and communications represent a fundamental shift in defensive capabilities, with early-stage companies attracting substantial venture capital.
Hypersonic technologies for both offensive and defensive applications are drawing significant government and private investment. The technical complexity and development costs create substantial barriers to entry whilst offering first-mover advantages to successful platforms.
Biotechnology applications in defense span from enhanced soldier performance to biological threat detection and response. These dual-use technologies offer compelling commercial applications alongside defense utility, expanding addressable markets significantly.
Space-based defense capabilities continue attracting substantial private capital, with satellite constellations, space-based sensors, and orbital manufacturing presenting multi-billion-dollar opportunities. The commercialisation of space creates multiple revenue streams beyond traditional government contracts.
Exit Strategy Evolution
Exit strategies for defense investments are evolving rapidly as both strategic acquirers and public markets show increased appetite for defense-focused businesses. Traditional prime contractors are actively acquiring innovative technologies and platforms to enhance their competitive positioning.
Technology giants including Microsoft, Amazon, and Google are expanding their defense footprints through acquisitions and partnerships, creating new exit pathways for defense-focused venture investments. These strategic acquirers bring substantial resources and commercial expertise to scaling defense technologies.
Public market appetite for defense businesses has improved significantly, with defense-focused SPACs and traditional IPOs attracting institutional investor interest. Recent successful public offerings demonstrate growing comfort with defense business models among public market investors.
Also secondary market activity is increasing as specialist defense funds mature and seek liquidity. The development of a robust secondary market provides additional exit flexibility for LPs seeking to adjust their defense exposure over time.
Strategic Implementation Framework
LPs considering defense investments should develop comprehensive implementation frameworks that address allocation, manager selection, and ongoing monitoring requirements. These frameworks must balance opportunity capture with appropriate risk management and stakeholder considerations.
Allocation frameworks should specify target exposure levels across different defense sub-sectors and geographic regions. Clear guidelines help ensure consistent decision-making whilst providing flexibility to adapt to changing opportunity sets and market conditions.
Manager selection criteria must evaluate both investment capabilities and defense-specific expertise. Successful defense investing requires understanding of procurement processes, regulatory requirements, and technology development cycles that differ significantly from commercial markets.
Risk Management Evolution
Risk management in defense investing continues evolving as the sector matures and institutional participation increases. Traditional risk assessment frameworks require enhancement to address unique defense-specific considerations including regulatory compliance, technology obsolescence, and geopolitical sensitivity.
Compliance monitoring systems must track export control regulations, security clearance requirements, and end-use restrictions across portfolio companies. Robust compliance frameworks protect against regulatory penalties whilst ensuring alignment with institutional values.
Technology risk assessment requires continuous evaluation of threat evolution and competitive dynamics. Defense technologies face unique obsolescence risks as adversaries develop countermeasures and new threats emerge requiring different solutions.
Practical Implementation Guidelines
LPs should begin defense investment considerations by establishing clear policy guidelines that address their specific circumstances and stakeholder requirements. These policies should specify acceptable investment types, geographic restrictions, and end-use limitations.
DD processes require enhancement beyond traditional private equity standards. Defense-specific due diligence must evaluate government relationships, security clearance capabilities, regulatory compliance frameworks, and technology differentiation.
Ongoing monitoring systems should track regulatory developments, geopolitical changes, and technology evolution that could impact portfolio performance. Regular reviews ensure continued alignment with institutional objectives and evolving risk tolerances.
Red Flags for LP Consideration
LPs should also be alert to several potential red flags when evaluating defense investment opportunities. GPs lacking security clearance capabilities or government contracting experience may struggle to execute successful defense strategies.
Investment targets with unclear end-use applications or customers in sanctioned jurisdictions present significant compliance risks. Weak ESG monitoring frameworks indicate potential reputational exposure that could impact institutional relationships.
Technologies with limited commercial applications face higher obsolescence risks and reduced exit optionality. Single-customer dependencies create concentration risks that may not align with institutional risk tolerances.
Geographic Strategy Considerations
Geographic diversification strategies should consider varying defense spending patterns, regulatory environments, and geopolitical risks across different markets. The US remains the largest defense market but with significant increases in Defense budgets Europe is increasingly stepping up and should provide good opportunities – also in the context of diversification.
Underscoring the importance and size of the US market Table 1, below, show the ten largest PE or VC backed investments in aerospace and defense since the 1st of January 2024. Notably, they were all North American as were the investors. Also worth noting that, compared to the more established PE / VC sectors, the deal sizes are relatively speaking quite small.
Table 1: Largest PE/VC-backed Investments in Aerospace and Defense, since the 1st of January 2024
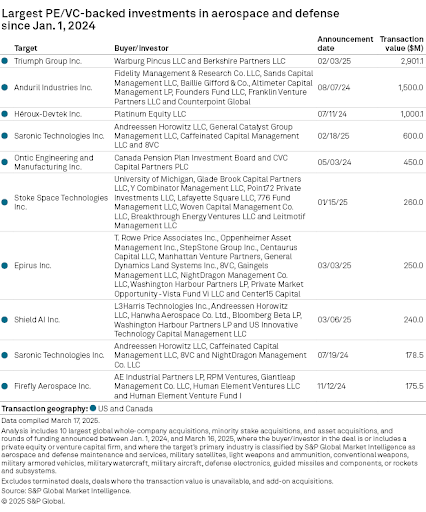
Source: S&P Global, March 2025
European defense spending is increasing significantly, see also Part 2, but requires navigation of different regulatory frameworks and procurement processes. Understanding these variations proves essential for successful cross-border defense investing.
Allied nation cooperation initiatives create opportunities for multinational defense ventures that leverage complementary capabilities and shared funding sources. These collaborations can reduce individual country exposure whilst accessing larger combined markets.
LP Action Items and Next Steps
LPs interested in defense exposure should begin by conducting portfolio reviews to identify existing defense-adjacent investments that may not be explicitly classified as defense assets. This analysis provides baseline exposure understanding before making additional allocations.
Given the somewhat specialized nature and risks of Defense investing LPs should also consider developing internal expertise through training programmes, external consultants, or advisory board appointments to build institutional capabilities for defense investment evaluation and monitoring. This expertise will likely be essential for successful programme implementation and mitigating various risks.
Engaging with existing manager relationships to understand their defense capabilities and interest levels can identify immediate opportunities without requiring new manager relationships. Many generalist managers have defense expertise that may not be prominently marketed.
Implementation Timeline Framework
LPs should consistently employ a strong framework to maintain a comprehensive market overview and a disciplined approach, whether re-evaluating existing investment strategies or exploring new sub-asset classes or industries. A straightforward yet effective framework is presented here.
- Months 1-3: Conduct portfolio analysis, develop policy frameworks, and establish internal expertise requirements. This foundation phase ensures appropriate preparation for active investment consideration.
- Months 4-6: Begin manager evaluation processes, attend defense-focused conferences, and develop a pipeline of potential opportunities. This market engagement phase builds understanding and relationship networks.
3. Months 7-12: Execute initial investments, establish monitoring frameworks, and refine policies based on early experience. This implementation phase translates planning into active investment programmes.
Orca Can Help Generate Long and Short-Lists of Defense GPs
To address the second point, we at Balentic have recognized the laborious and unnecessarily repetitive process LPs undergo when generating and enriching long-lists to narrow down to a short-list. Therefore, we have established Defense as a distinct theme on Orca.
We are currently mapping the defense investment landscape and onboarding GPs onto our platform. This will allow LPs to easily search for defense opportunities,and refine by geography, sub-asset class, and stage. LPs can then generate enriched long and short-lists and directly contact GPs of interest.
Future Outlook and Conclusions
The defense investment landscape will continue evolving as geopolitical tensions persist and technological advancement accelerates. Private market participants who develop sophisticated defense investment capabilities will be well-positioned to capture attractive opportunities.
LP acceptance of defense investments will likely continue expanding as stakeholders recognise the sector’s role in supporting stability and democratic values. This acceptance creates opportunities for early movers whilst the sector remains underallocated.
The convergence of private market dynamism and strategic defense needs represents a generational investment opportunity. Success requires sophisticated execution but offers the potential for attractive returns whilst supporting national security objectives.
Defense investing has transformed from a niche specialty to a mainstream institutional consideration that demands professional execution and careful risk management. Those who approach it thoughtfully will find compelling opportunities to generate returns whilst contributing to global stability.
Conclusion: From Transformation to Implementation
Defense investing’s transformation from taboo to strategic theme represents one of the most significant shifts in private market investing in recent years. As geopolitical tensions continue reshaping global priorities, defense investing will likely become an increasingly important component of sophisticated LP portfolios.
The investment opportunity spans multiple asset classes and strategies, from early-stage venture investments in dual-use technologies to infrastructure investments in critical defense assets. Success requires solid understanding of regulatory requirements, stakeholder considerations, and risk management practices.
For LPs, the question is no longer whether defense investing belongs in institutional portfolios, but rather how to approach it responsibly and effectively. Those who develop clear frameworks, select appropriate managers, and maintain high standards for governance will be best positioned to succeed.
The sector’s evolution creates compelling opportunities for LPs seeking exposure to technological innovation, government-backed revenue streams, and thematic alignment with national security priorities. With appropriate execution, defense investing can support peace, resilience, and stability whilst generating robust private market returns.
The time for theoretical consideration has passed. LPs must now develop practical frameworks for defense investment participation or risk missing one of the most significant thematic opportunities in private markets. The convergence of strategic necessity and investment attractiveness creates a compelling case for action.
Stay Illiquid
Kasper
More Insights
Balentic Edge
Sign up to keep up to date with the latest news and updates.
© 2025 Balentic ApS. CVR: 44034255. All rights reserved.
Privacy Policy | Terms of Service
The Balentic website and Orca are, and are expected to continue to be, under development. Consequently, some of the features described in this Overview and/or on the website may not yet be available or may work differently. Some features may furthermore not be available to all users.


